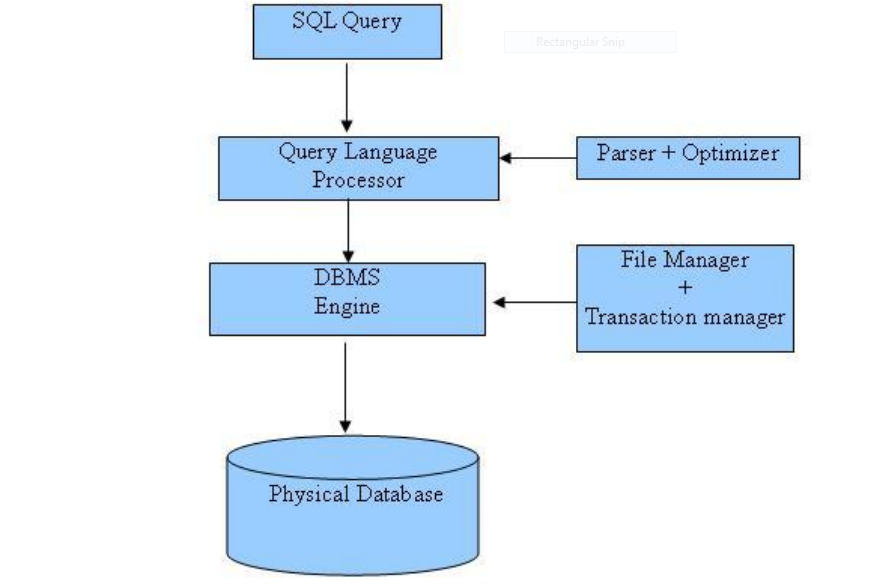
RDBMS
stands for Relational Database Management System. It is the basis of
SQL and is used in all the modern
database systems. A RDBMS is basically a DBMS(Database Management System )that
maintains records between the tables and is based on the Relational Model by
E.F. Codd.
Table:
The data in database is stored in the
form of database objects known as tables. Table consist of rows and columns .
It is a collection of related data items.
Emp_Id
|
Name
|
Age
|
Dept
|
01
|
Gpsingh
|
20
|
Programming
|
02
|
Mpsingh
|
19
|
Web desiging
|
Field: Field is
nothing just the columns of the table. In the above table Emp_Id, Name,Age,Dept
are the fields of the table.
Row: A row is
also called as a record or the row of data.
A row can consist of data of different datatypes. The data in the row
can have values of different fields of different datatypes . Following is a
simple row from the above table.
01
|
Gpsingh
|
20
|
Programming
|
Column:
A column is a vertical entity in a table
that contain all the information of the data of a specific data type. Each
column has its own data type and it can store data of that particular datatype
only.
Following is the example of a column from
the above table
Name
|
Gpsingh
|
Mpsingh
|
Null Value:
A null value means a value that appears
blank in the database. The null value is different from the zero value or blank
spaces. The zero value or blank spaces are themselves value but a null value measn
that there is no value and that field in database is blank.
SQL Constraints:
Constrains means the rules that are
enforced on the columns of the table. When inserting values in the database
these constraints are checked to validate the entries to be stored in the
database. The main benefit of constraints is that they enforce the accuracy and
reliability of the database.
Types of constraints:
1. Column Level Constraints
2. Table Level Constraints
Commonly used constraints in SQL:
Constraint
|
Purpose
|
NOT
NULL Constraint
|
Ensures
that a column cannot have NULL value.
|
DEFAULT
Constraint
|
Provides
a default value for a column when none is specified.
|
UNIQUE
Constraint
|
Ensures
that all values in a column are different
|
PRIMARY
Key
|
Uniquely
identified each rows/records in a database table.
|
FOREIGN
Key
|
:
Uniquely identified a rows/records in any another database table.
|
CHECK
Constraint
|
The
CHECK constraint ensures that all values in a column satisfy certain conditions.
|
INDEX
|
Use
to create and retrieve data from the database very quickly
|
:
Categories of Data Integrity:
1.
Entity Integrity : It means that there cannot be any duplicate row in the
table having values of all the fields same as that of some other row in the
same table.
2.
Domain Integrity : Its main focus is to check for that valid data. The data
to be entered in some field may be required in some range. Eg: for applying for
a vacancy of a job the date of birth may be required between required within in
the two yeas rangle.
3.
Referential Integrity : The rows that are being used by some other records cannot
be deleted. The value of the records may be dependent on that record. So, Until
the dependency exist the records cannot be deleted.
4.
User-Defined Integrity
: Enforces some specific business
rules that do not fall into entity, domain, or referential integrity